UCT's Computational Biology group has been using the ICTS HPC cluster to investigate Bipolar Disorder predisposition. Below Gerrit Botha gives a summary of the methods used.
Bipolar Disorder (BPD) is a severe psychiatric illness, characterised by extremes in mood whereby affected individuals may experience episodes of both mania and depression. Studies have shown that BPD has heritability estimates ranging from 59% to 85% and that first degree relatives and half-siblings of affected individuals are at a significantly increased risk of developing the disorder. As part of the PhD project entitled Analysis of genetic overlap in three psychiatric phenotypes, we undertook whole genome sequencing for four related individuals affected with BPD. The whole-genome sequencing was carried out at the University of Southern California, using the Illumina Genome Analyzer IIx (GAIIx) and Illumina HiSeq2000 systems. This technology is based on a proprietary reversible terminator based method which is able to detect single nucleotides as they are incorporated into growing DNA strands. The aim of this investigation is to identify novel genetic variants predisposing individuals to BPD.

A complete variant analysis pipeline was setup on the UCT HPC cluster. The workflow is as follows (see Diagram 1). Raw reads are checked for quality and if necessary filtered out. The remaining reads are mapped to the human reference build (hg19). Post-processing involves the removal of duplicate mappings, selecting properly mapped reads (both the forward and
reverse read needs to be present), realignment around indels (insertions and deletions) and recalibration of quality scores. A list of SNPs (Single-nucleotide polymorphisms) and indels are then generated using the variant calling software. These SNPs and indels are then annotated according to gene region, novelty, function and percentage of functional importance. The fully annotated list can then be analysed using variant analysis software and genome browsers.
The pipeline consisted of well known NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) tools and they were successfully integrated into the cluster:
- FASTQC – Quality control
- FASTX-toolkit – Fltering and trimming
- BWA – Mapping
- SAMTOOLS – Post-processing and variant calling
- Picard – Post-processing
- GATK – Realignments, recalibrating and variant calling
- VCFtools – Post-processing
- ANNOVAR – Annotation
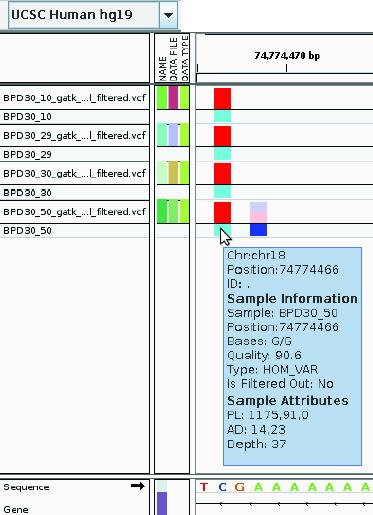
The processed data is currently being analysed using external tools such as SVA (Sequence Variant Analyser), IGV (integrated genome viewer) and Galaxy. For example Figure 1 below displays an insertions detected within all samples. Cases like this are now being investigated to determine their overall importance.